Starting a solar energy business is an incredible opportunity for those passionate about sustainability and renewable energy!
It’s an amazing venture that merges innovation with purpose.
However, turning that vision of a green future into a profitable solar business requires more than just a passion for clean energy. It demands a well-structured business plan to tackle market challenges and manage your resources efficiently.
Curious about how to put one together?
No need to stress! This detailed guide and free solar business plan template will set you on the right path. Let’s get started!
What is a solar panel business plan?
A solar business plan is a formal document that details the strategic approach, financial outlook, and operational framework of a solar energy company.
It helps with the business objectives, overall market analysis, target customers, services, or product ranges- such as systems of solar panels, maintenance, or power solutions, promotional activities, and company structure. Also, other factors relating to solar.
This plan acts as a comprehensive blueprint for starting and scaling a solar energy business within a competitive and eco-friendly marketplace.
Why create a business plan for solar panels?
Having a solar business plan is the foundation of your solar energy business.
Here’s why:
- When you write a solar business plan, you force yourself to think through your business goals, target market, market needs, and services. This will give your solar business a clear direction and make it viable and sustainable.
- Funding is key to starting or growing your solar business. A business plan is often required by investors and lenders and provides a clear picture of your business’s profitability. They want to know how your solar business makes money and how you will deliver a return on investment.
- A business plan is a guide for your daily operations, it helps you streamline processes like sourcing materials, managing installation teams and maintaining solar infrastructure. It also sets up the framework for customer service and maintenance.
- Solar businesses face specific challenges like changing regulations, equipment costs, or weather-related impacts. With a solar business plan you can anticipate these risks and have strategies in place to deal with them so your business can adapt and grow.
With these advantages in mind, it’s time to explore how to build your solar business plan to set your business up for success.
How to write a solar panel business plan
When writing a solar panel business plan, it's important to cover all the key aspects of your business. Here’s a detailed guide on what to include:
Executive summary
An executive summary is the most important part of a solar business plan because it provides a snapshot of what your solar company is all about.
Although it comes first in the plan, it’s best to draft it after you’ve completed all other sections. This approach helps you give a well-rounded, clear summary of your business.
Keep the language simple, avoid complex terms, and make it engaging to spark interest.
In this section, you’ll want to focus on the following points:
- Your solar company's name and where it operates
- Your mission and vision for the business
- The business model and its current status (new business or established)
- The market potential and who your target customers are
- What sets your solar business apart from others
- The strategies you’ll use to promote and grow your business
- Key financial details (e.g., projected earnings and profitability)
In short, your executive summary should give readers a clear, concise overview that draws them into your plan.
Liking the plan you're reading? It's AI generated.
Generate Your Own Using Bizplanr AI
Company overview
The company overview section gives a comprehensive picture of your solar business, covering everything from its foundational principles to future aspirations.
Here’s your chance to dive deeper into the business concept and ensure that readers—whether potential investors, customers, or partners—understand your vision clearly.
This section should highlight the following:
- A detailed explanation of your solar services
- Legal structure (LLC, corporation, etc.)
- Founders and key team members (if applicable)
- Type of services you offer (residential, commercial, or both)
- The backstory of your business (how and why it began)
- Significant milestones or achievements thus far
- Short-term and long-term goals for the business
Discussing your business location is important, as it can impact your customer base, local regulations, and even solar energy demand in the region.
In summary, the company overview provides a well-rounded understanding of your solar business, helping to establish trust and credibility. Keep it clear, informative, and engaging.
Industry analysis
In the industry analysis section, you'll need to provide an in-depth overview of the solar energy market that your business will operate in.
While this might seem like extra work, it brings several benefits.
Thorough market research helps you position your solar business within the broader renewable energy industry. It also allows you to grasp current trends, understand your target audience, and analyze your competition.
Here are some key questions to address in this section:
- What is the global scale of the solar energy market?
- How large is the U.S. solar industry? Is it expanding or shrinking?
- How much potential growth has been identified in the market within the next 5-10 years?
- What are some of the new trends or developments in the solar market emerging recently?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- What are some of the key factors that may influence the solar market given ever increasing regulation or environmental policy?
Ensure you back up your analysis with solid research and actual data to provide a well-rounded understanding of the industry.
Competitive analysis
The competitive analysis focuses on the local solar energy market and examines how your business will stand out from the competition.
By understanding your competitors' strengths, weaknesses, pricing approaches, and customer base, you can uncover opportunities and shape strategies that set your business apart.
Here’s a guide to structuring this section:
- Identify both direct and indirect competitors in your area
- Evaluate what your competitors are doing well and where they have room for improvement
- Review their pricing models and how they approach customer relationships
- Analyze the customer experience offered by other solar companies
- Compare the services you offer and identify any unmet needs in the market
In addition to this, explain your business's unique strengths and how you’ll use them to create a competitive edge.
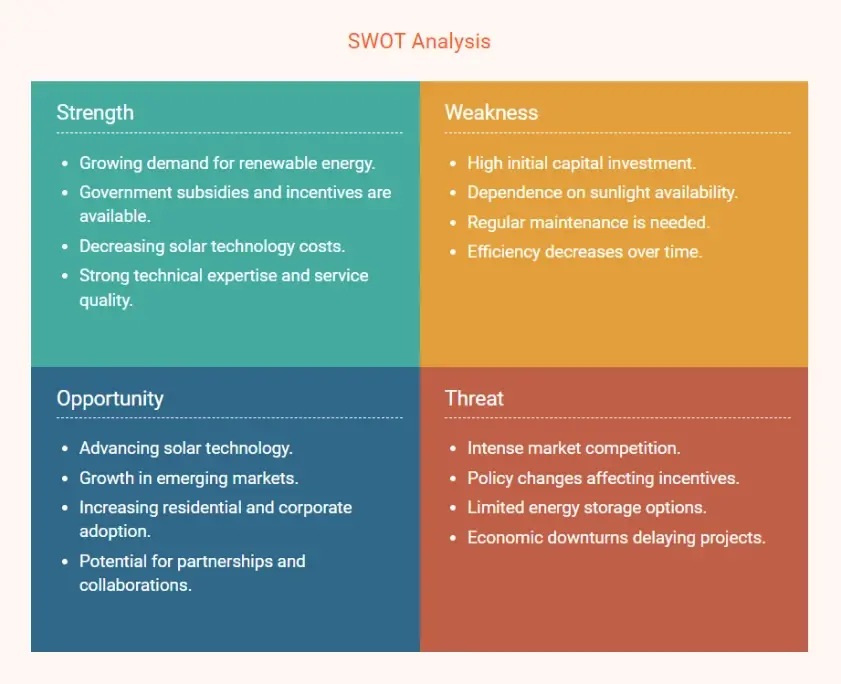
By doing this, you'll show investors and stakeholders that you're aware of the market landscape and have a clear plan to rise above the competition.You can also consider creating a SWOT analysis.
Here is an example:
Solar services and products
In this section, provide a detailed overview of the solar energy services and products your business plans to offer.
Clearly outline the range of services you’ll provide, such as installation, maintenance, or energy audits, along with the products, like solar panels or battery storage systems. Also, try to include pricing details and how you plan to meet your customers’ needs.
For example, your service offerings may include:
- Residential solar panel installation
- Commercial solar energy systems
- Solar system maintenance and repair
- Energy storage solutions (batteries)
- Solar energy consultations and audits
Team and management
Whether you have a small solar business or a bigger team, having a clear management structure is key to success in the solar industry.
In this section introduce the key people in your business, including the owners, managers, lead technicians and any other important team members. Make sure to outline their roles, responsibilities, experience and expertise and how each contributes to the overall success of your company.
For example:
- Owners/Partners Project managers for installations
- Lead solar technicians and engineers
- Customer support and sales teams
- Installation crews
Then introduce any advisors or consultants that advise your business.
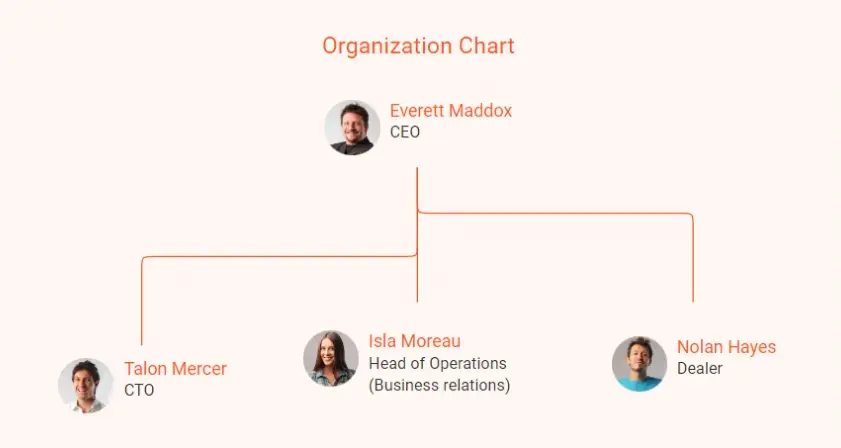
Finally, present a chart to show how the key people in the company connect and work together. This will give a clear view of the leadership and management structure.
Example:
Sales and marketing
In this section, you'll outline how your solar business will attract customers and generate leads, ultimately driving more revenue.
You’ll need to create marketing and sales strategies that show your target audience and highlight the unique strengths of your solar services. These strategies will help bring in new clients and keep them engaged with your business.
Here are a few sales and marketing tactics for a solar business:
- Use social media platforms to showcase successful solar installations and customer testimonials
- Offer referral programs that reward customers for recommending your services
- Partner with local home builders, architects, or environmental groups
- Create a professional, SEO-optimized website to attract online traffic and leads
- Advertise on solar industry directories, renewable energy websites, and through Google Ads
- Attend local business expos, energy trade shows, or community events to network and raise awareness
Additionally, consider offering limited-time promotions, loyalty programs for repeat customers, or discounts for customers who install solar during peak seasons.
Operations plan
The operations plan outlines how your solar business will function on a daily or weekly basis, ensuring smooth management of all operational aspects.
A well-thought-out operations plan clarifies the workflow and processes that are important to the quality of your services.
In this section, you’ll want to cover the following key elements:
- Business hours and availability for solar consultations or installations
- Scheduling systems for client appointments and project timelines
- Customer service processes, including response times and support protocols
- Inventory and supply management for solar panels, tools, and equipment
- Maintenance of equipment and vehicles used in installations
- Any technology or systems used for project management, customer communication, and monitoring
By addressing these aspects, you demonstrate to stakeholders that your solar business has a solid operational plan in place to consistently deliver high-quality services.
Financial projections
To build a profitable solar business, it’s essential to have a comprehensive financial plan with realistic projections.
This plan should outline the financial aspects of your business, typically presented on a monthly or quarterly basis, and show how you will achieve your financial goals over the first 3-5 years.
Here are some key financial statements and reports you should include in your solar business financial plan:
Profit and loss statement (Income statement)
| Category | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | |||
| - Product Sales | 1,000,000 | 1,500,000 | 2,250,000 |
| Total Revenue | 1,000,000 | 1,500,000 | 2,250,000 |
| COGS (Cost of Goods Sold) | |||
| - Parts & Supplies | 600,000 | 900,000 | 1,350,000 |
| - Travel & Fuel Costs | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total COGS | 600,000 | 900,000 | 1,350,000 |
| Gross Profit | 400,000 | 600,000 | 900,000 |
| Operating Expenses | |||
| - Rent (Office Space) | 180,000 | 180,000 | 180,000 |
| - Insurance | 20,000 | 20,000 | 20,000 |
| - Licenses & Permits | 5,000 | 5,000 | 5,000 |
| - Marketing & Advertising | 50,000 | 75,000 | 112,500 |
| - Wages (Technician Salary) | 120,000 | 120,000 | 120,000 |
| Total Operating Expenses | 375,000 | 400,000 | 437,500 |
| Net Operating Income (Loss) | 25,000 | 200,000 | 462,500 |
Cash flow statement
| Category | Year 1 ($) | Year 2 ($) | Year 3 ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Cash Flow | |||
| - Net Income | 64,000 | 196,000 | 394,000 |
| - Depreciation | 40,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 |
| - Changes in Working Capital | 0 | -50,000 | -50,000 |
| Total Operating Cash Flow | 104,000 | 236,000 | 384,000 |
| Investing Cash Flow | |||
| - Purchase of Equipment | -200,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Total Investing Cash Flow | -200,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Financing Cash Flow | |||
| - Loan Proceeds | 500,000 | 0 | 0 |
| - Loan Repayment | -50,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Total Financing Cash Flow | 450,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Net Cash Flow | 354,000 | 186,000 | 384,000 |
Balance sheet for the end of year 3
| Category | Value ($) |
|---|---|
| Assets | |
| - Cash | 300,000 |
| - Accounts Receivable | 200,000 |
| - Equipment (after depreciation) | 120,000 |
| Total Assets | 620,000 |
| Liabilities | |
| - Loan Payable | 500,000 |
| - Accounts Payable | 100,000 |
| Total Liabilities | 600,000 |
| Equity | |
| - Retained Earnings | 394,000 |
| Total Liabilities and Equity | 620,000 |
Download the solar panel business plan template
Are you ready to create your own solar panel business plan but need some extra help? No need to worry; we’ve got you covered. Here’s a free solar panel business plan PDF template for a solar business plan to get you started.
This template is specifically designed for entrepreneurs looking to develop a strong solar business plan. Just download it, fill in your details, and modify it to suit your specific requirements.
Conclusion
Now that you understand all the key components of a solar panel business plan, you’re ready to draft your own comprehensive plan.
If you have any questions about how to structure your plan or need further assistance, consider using a Free AI business plan generator. It can help you quickly create an actionable and effective solar business plan.
So, don’t hesitate—begin planning your solar panel business today!
Get Your Business Plan Ready In Minutes
Answer a few questions, and AI will generate a detailed business plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
How profitable is a solar panel business?
A solar panel business can be very profitable, especially with the growing demand for renewable energy. Profitability depends on your location, market, and the scale of your operations, but many businesses see solid returns due to tax incentives and reduced costs over time.
How much does it cost to write a solar panel business plan?
The cost of writing a solar panel business plan varies. If you do it yourself, it could just take time and effort. Depending on the complexity, hiring a professional could cost anywhere from $500 to $2,000.
For more detailed insights, check out this article on How Much Does a Business Plan Cost - Free vs Paid Options to explore various pricing options.
How do you get funding for your solar business?
There are various options available to fund your solar business. A few options to explore include:
- Bank loans
- Government grants
- Crowdfunding
- Investors
Where can you find business plan writers for your solar power business?
You can find business plan writers on freelance platforms like Upwork and Fiverr or through business consultancy firms that specialize in renewable energy projects.